Linux 防火墙
概念
Linux防火墙是由Netfilter组件提供的,NetFilter工作在内核空间,集成在Linux内核中,
而iptables只是一个工作在用户空间的一个命令行工具,用来编写规则,写好的规则被送往netfilter,
告诉内核如何去处理信息包
数据包过滤匹配流程
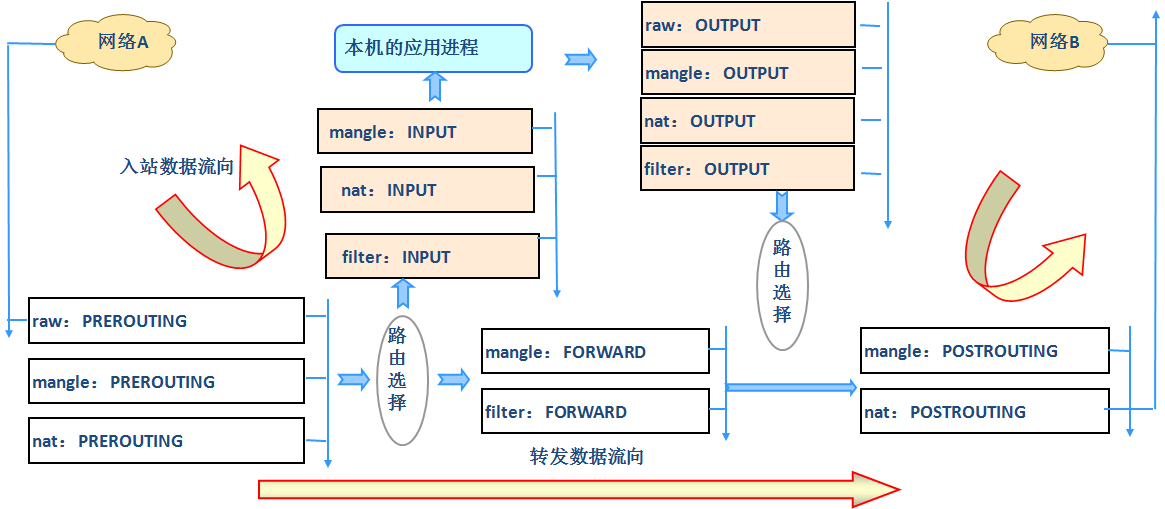
netfilter的5表和5链
netfilter 提供了五种表,每种表用于处理不同类型的数据包决策:(优先级从上到下增加)
- Filter Table:最常用的表,用于决定数据包的命运,如允许或阻止数据包通过。
- NAT Table:用于网络地址转换,如源NAT(SNAT)和目标NAT(DNAT)。
- Mangle Table:用于修改数据包的服务质量(QoS)标记和其他包头信息。
- Raw Table:用于设置不需要由连接跟踪系统处理的数据包。
- Security Table:用于设置强制访问控制(MAC)安全规则,通常与 SELinux 安全策略配合使用
五链,每个表包含几个预定义的链(内置链),数据包根据其流向和处理需求经过不同的链:
- INPUT:处理到达本机的数据包。
- OUTPUT:处理由本机发出的数据包。
- FORWARD:处理穿过本机(路由)的数据包。
- PREROUTING:用于在路由决策之前处理进入的数据包(主要用在 NAT 表)。
- POSTROUTING:用于在路由决策之后处理即将离开的数据包(主要用在 NAT 表)。
iptables 查看规则
iptables -S #查看更加详细的配置信息
iptables -vnL -t filter #默认filter
iptables -vnL -t filter --line-numbers #显示规则行号
iptables设置规则
数据包从PREROUTING 流入,POSTROUTING 流出,中间经过链条,按照链条所属的表优先级从高到低处理 在每个表内,例如filter表,INPUT链,那么按照filter表的INPUT链上的规则从上到下匹配处理,符合匹配, 就处理,不匹配就继续往下匹配规则,直到规则走完
基本匹配(不需要使用额外模块)
iptables [-t table] SUBCOMMAND chain [-m matchname [per-match-options]] -j targetname [per-target-options]
-t 哪个表 管理命令 那条链 哪个模块 具体匹配条件和选项 处理动作
管理命令 :
-N:new, 自定义一条新的规则链
-E:重命名自定义链;引用计数不为0的自定义链不能够被重命名,也不能被删除
-X:delete,删除自定义的空的规则链
-P:Policy,设置默认策略;对filter表中的链而言,其默认策略有:ACCEPT:接受, DROP:丢弃
范例:
iptables -N test-chain -t filter
iptables -E test-chain test1-chain
iptables -X test1-chain
#往自定义链条添加规则
iptables -t filter -A web -s 10.0.0.3 -j DROP
#在内置链条上引用自定义链
iptables -A INPUT -j web
-A:append,追加
-I:insert, 插入,要指明插入至的规则编号,默认为第一条
-D:delete,删除
(1) 指明规则序号
(2) 指明规则本身
-R:replace,替换指定链上的指定规则编号
-F:flush,清空指定的规则链
-Z:zero,置零
iptables的每条规则都有两个计数器
(1) 匹配到的报文的个数
(2) 匹配到的所有报文的大小之和
基本条件
[!] -s, --source address[/mask][,...]:源IP地址或者不连续的IP地址
[!] -d, --destination address[/mask][,...]:目标IP地址或者不连续的IP地址
[!] -p, --protocol protocol:指定协议,可使用数字如0(all)
protocol: tcp, udp, icmp, icmpv6, udplite,esp, ah, sctp, mh or“all“
参看:/etc/protocols
[!] -i, --in-interface name:报文流入的接口;只能应用于数据报文流入环节,只应用于INPUT、FORWARD、PREROUTING链
[!] -o, --out-interface name:报文流出的接口;只能应用于数据报文流出的环节,只应用于FORWARD、OUTPUT、POSTROUTING链
iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.6,10.0.0.10 -d 10.0.0.100,10.0.0.200 ! -p icmp -i eth0 -j REJECT
扩展匹配
隐式扩展模块
iptables 在使用-p选项指明了特定的协议时,无需再用-m选项指明扩展模块的扩展机制,不需要手动加载扩展模块
tcp 协议的扩展选项
[!] --source-port, --sport port[:port]:匹配报文源端口,可为端口连续范围
[!] --destination-port,--dport port[:port]:匹配报文目标端口,可为连续范围
[!] --tcp-flags mask comp
mask 需检查的标志位列表,用,分隔 , 例如 SYN,ACK,FIN,RST
comp 在mask列表中必须为1的标志位列表,无指定则必须为0,用,分隔tcp协议的扩展选项
范例:
--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN #表示要检查的标志位为SYN,ACK,FIN,RST四个,其中SYN必须为1,余下的必须为0,第一次握手
--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN,ACK #第二次握手
#错误包
--tcp-flags ALL ALL
--tcp_flags ALL NONE
udp 协议的扩展选项
[!] --source-port, --sport port[:port]:匹配报文的源端口或端口范围
[!] --destination-port,--dport port[:port]:匹配报文的目标端口或端口范围
icmp 协议的扩展选项
[!] --icmp-type {type[/code]|typename}
type/code
0/0 echo-reply icmp应答
8/0 echo-request icmp请求
iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.6 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j REJECT
显式扩展及相关模块
显示扩展即必须使用-m选项指明要调用的扩展模块名称,需要手动加载扩展模块
multiport扩展
以离散方式定义多端口匹配,最多指定15个端口
[!] --source-ports,--sports port[,port|,port:port]...
[!] --destination-ports,--dports port[,port|,port:port]...
[!] --ports port[,port|,port:port]...
iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.0/16 -d 172.16.100.10 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 20:22,80 -j ACCEPT
iprange扩展
[!] --src-range from[-to] 源IP地址范围
[!] --dst-range from[-to] 目标IP地址范围
iptables -A INPUT -d 172.16.1.100 -p tcp --dport 80 -m iprange --src-range 172.16.1.5-172.16.1.10 -j DROP
mac扩展
iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.100 -m mac --mac-source 00:50:56:12:34:56 -j ACCEPT
string扩展
对报文中的应用层数据做字符串模式匹配检测
--algo {bm|kmp} 字符串匹配检测算法
bm:Boyer-Moore
kmp:Knuth-Pratt-Morris
--from offset 开始偏移
--to offset 结束偏移
[!] --string pattern 要检测的字符串模式
[!] --hex-string pattern 要检测字符串模式,16进制格式
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --sport 80 -m string --algo kmp --from 62 --string "google" -j REJECT
iptables规则保存
使用iptables命令定义的规则,手动删除之前,其生效期限为kernel存活期限
持久保存
CentOS 7,8
iptables-save > /PATH/TO/SOME_RULES_FILE
CentOS 6
#将规则覆盖保存至/etc/sysconfig/iptables文件中
service iptables save
加载规则
CentOS 7,8 重新载入预存规则文件中规则:
iptables-restore < /PATH/FROM/SOME_RULES_FILE
iptables-restore选项
-n, --noflush:不清除原有规则
-t, --test:仅分析生成规则集,但不提交
CentOS 6:
#会自动从/etc/sysconfig/iptables 重新载入规则
service iptables restart
开机自动加载
1.脚本写到 /etc/rc.d/rc.local 执行
2.定义Unit File, CentOS 7,8 可以安装 iptables-services 实现iptables.service
[root@centos8 ~]#yum -y install iptables-services
[root@centos8 ~]#cp /etc/sysconfig/iptables{,.bak}
#保存现在的规则到文件中方法1
[root@centos8 ~]#/usr/libexec/iptables/iptables.init save
#保存现在的规则到文件中方法2
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables
#开机启动
[root@centos8 ~]#systemctl enable iptables.service
[root@centos8 ~]#systemctl mask firewalld.service nftables.service
NAT
NAT: network address translation,支持PREROUTING,INPUT,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING四个链
SNAT
source NAT ,支持POSTROUTING, INPUT,让本地网络中的主机通过某一特定地址访问外部网络,实现地址伪装,请求报文:修改源IP
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.0/24 ! -d 10.0.0.0/24 -j MASQUERADE #公网不固定
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.0/24 ! -d 10.0.0.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 192.168.0.8 #公网固定
#查看转换状态信息
cat /proc/net/nf_conntrack
DNAT
destination NAT 支持PREROUTING , OUTPUT,把本地网络中的主机上的某服务开放给外部网络访问(发布服务和端口映射),但隐藏真实IP,请求报文:修改目标IP
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.0.8 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.0.7:8080
REDIRECT
本机重定向,将发往本机的数据包,从一个端口从定向到另一个端口
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080